The domain of Attacks
Software
Hardware
Attack Model
CAPEC-233: Privilege Escalation
CWE-ID: – 1272
Hardware-based isolation and access control (e.g., identity, policy, locking control) of sensitive shared hardware resources such as registers and fuses, and information leakage.
Threat Model – Privilege Escalation
| Soc Vul. # | Name of Core | Security Requirement | Threat model description | Effect | SW attack model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | CVA6 RISC-V CPU | The privilege level should not be changed during a complete instruction execution | Privilege Escalation: Privilege level switched to lower privilege levels during the execution of an instruction | Changing the privilege level during an instruction can update the micro-architectural state to control and data registers (CSR) | Software in the guest OS can alter the privilege level during an instruction. Possible attacks: Access control, Illegal interrupt, information leakage etc |
Description
In a system-on-chip (SoC), the software will commonly access the peripherals through a memory-mapped register interface. Thus, the software can access only certain registers with respect to their privilege level hardcoded in the design. However, through the accessible register interface, malicious software could tamper with the hardware data. During the execution of an instruction, the privilege level should not be altered. Changing the privilege level during this can lead to access control violations and possible integrity loss.
Security Property
| property priv_viol; @(posedge clk_i) disable iff (!rst_ni) ( ariane.csr_regfile_i.privilege_violation) |-> (~ariane.csr_regfile_i.csr_we && ~ariane.csr_regfile_i.csr_read ); |
Procedure
- Invoke Cadence JG inside the cva6_master folder
- Run the prove_t1.tcl script to check the assertion.
- Violation in the assertion will generate CEX.
Impact of Vulnerability
Loss of confidentiality and integrity of the SoC
Severity
TBA (Metrics to evaluate the vulnerability impact)
tools used
Cadence JasperGold
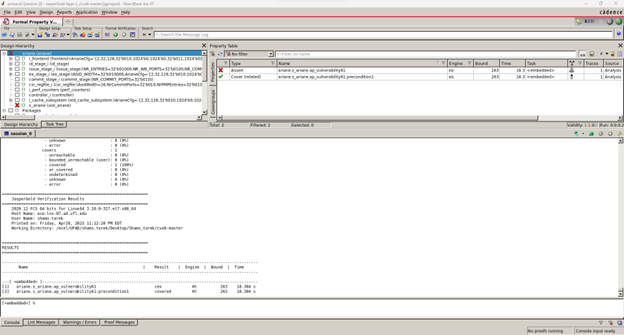
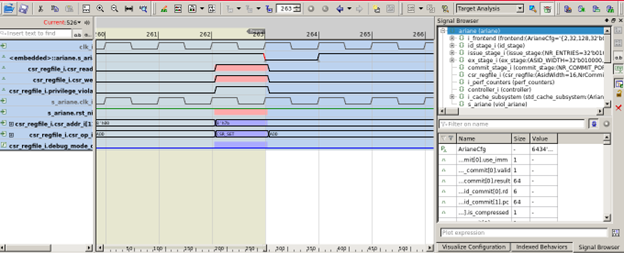
Results (counter-example)
Fig.1 shows that the property (ref. Table.2) violates the RISC-V design, indicating the read/write state change (privilege violation) in the generated CEX (shown in Fig.2).